| Home > China Feature |
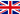
Earthen Pot (沙锅 Shaguo)
The earthen pot is commonly used in China both as a cooking utensil and a table vessel. Various soups made in such a pot with vegetables and meatballs and/or soya bean curd are inexpensive, tasty and therefore highly popular.
The Chinese earthen pot is made of a special white pottery clay which, with its stable chemical property, is impregnable to acid, alkaline or salt. It is superior in several ways to cooking vessels of iron or aluminium. Food cooked or stored away in the clay casserole will not easily deteriorate in the heat of summer.
.jpg)
Clay pots of a smaller size are also used by the Chinese to boil medicinal herbs, as they do not add any extraneous substance to the resultant decoction.
Most of the earthen pots come from two sources Foshan area in Guangzhou and Yixing area in Jiangsu Province. The sandy clay in these places makes an ideal material for the pottery industry. "shiwan sanbao" produced at Shiwan in Foshan city, Guangdong Province, are sold to Hongkong, Macao and Southeast Asia. It is a cooker (bao) that can be used for triple (san) purposes to cook rice, to make gruel and to boil tea.
Being made of burnt clay, the earthen pot is easily breakable and must be handled with care. It must not be heated on the fire when it contains no liquid inside; otherwise, it will crack and become leaky. A new pot, before being used, should be soaked in cold water for three to four hours and then heated over a fire to bring the water to a boil two or three times; this will temper the clay and give it a higher degree of hardness.
The clay pot is a slow heat-conductor, and that is why it keeps the food warm for a long time on the table in winter. When used in cooking, however, it should be heated first by a slow fire before intense heat is applied. When it is removed from the fire, it should be placed on a mat or wooden board, not direct on something damp and cold, for sudden contact with a cold surface may cause the hot pot to crack.
Art
 more
moreChina Beijing International Diet ...
Recently, The hit CCTV documentary, A Bite of China, shown at 10:40 ...

Exhibition of Ancient Chinese Jad...
At least 8,000 years ago, Chinese ancestors discovered a beautiful...

Longmen Grottoes
The Longmen Grottoes, located near Luoyang, Henan Province, are a tr...

Custom
 more
moreWeb Dictionary
Martial Arts
Tai Chi Master Class Held in Moscow
MOSCOW, June 15, 2016 (Xinhua) -- Students learn from Shaolin ...
Celebriting 70 years' efforts in restoring Mogao...
Work is being carried out at the restoration site of cave No 98 a...
Hong Kong Children's Symphony performs in Seattle
Under the theme of Tribute to the Golden Age, a concert featuring a ...





 print
print  email
email  Favorite
Favorite  Transtlate
Transtlate